Detailed Description for Each Topic in “Components of Food”
1. Introduction to Food and Nutrition:
- Food: The primary source of nutrients necessary for the growth, maintenance, and functioning of our bodies.
- Nutrition: The process of consuming and using food substances for energy, growth, and maintaining health.
- Variety of Meals: Meals can differ by region but generally include a mix of grains, vegetables, proteins, and fats to provide a balanced intake of nutrients.
2. Types of Nutrients:
- Carbohydrates:
- Function: Provide energy to the body.
- Types: Simple (sugars) and complex (starches).
- Examples: Rice, wheat, potatoes, bread.
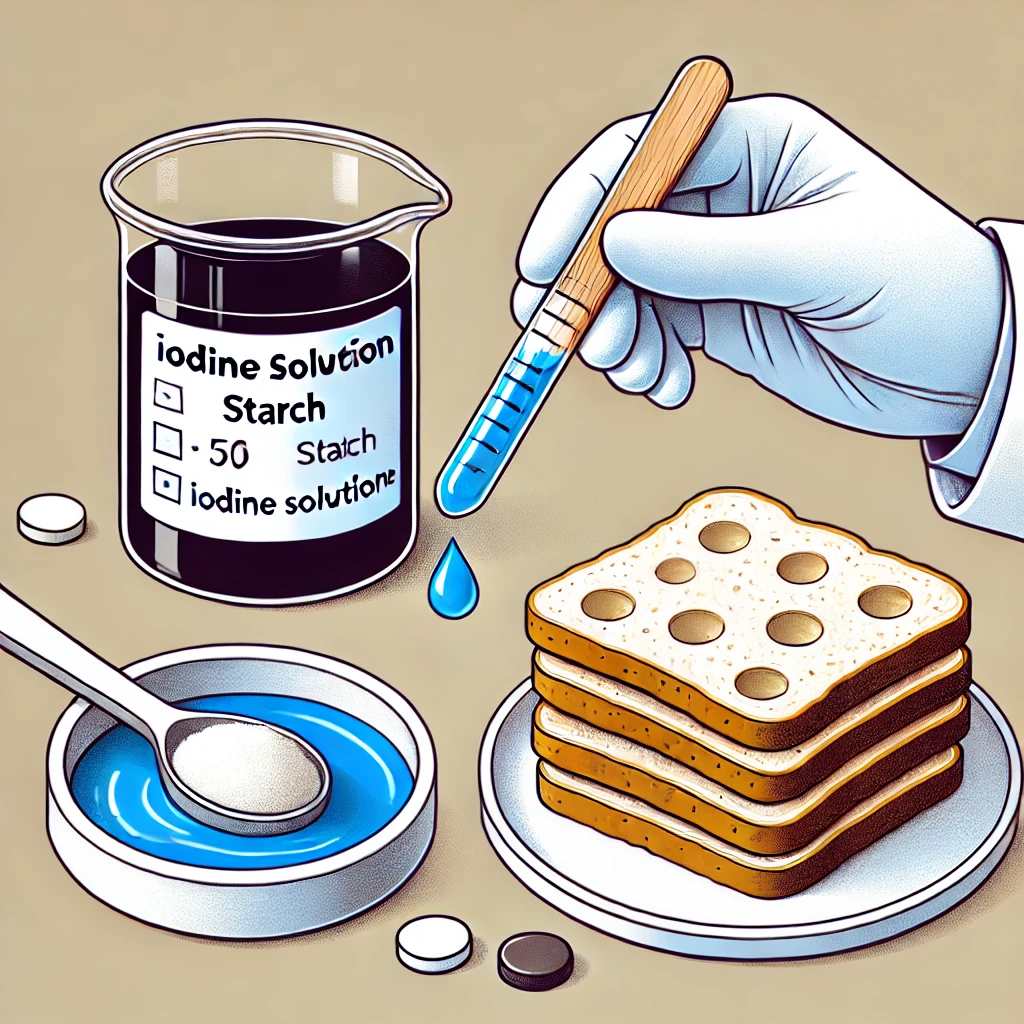
- Test: Iodine test for starch (turns blue-black).
- Proteins:
- Function: Essential for growth, repair, and maintenance of body tissues.
- Sources: Animal (meat, eggs, dairy) and plant (beans, lentils, nuts).
- Test: Biuret test (copper sulphate and caustic soda; turns violet).
- Fats:
- Function: Provide concentrated energy and help in the absorption of vitamins.
- Types: Saturated (animal fats) and unsaturated (plant oils).
- Examples: Butter, oils, nuts, cheese.
- Test: Oily patch on paper indicates fat presence.
- Vitamins:
- Vitamin A:
- Function: Maintains healthy vision and skin.
- Sources: Carrots, sweet potatoes, liver, spinach.
- Vitamin B:
- Function: Energy production, brain function, and cell metabolism.
- Sources: Whole grains, meats, eggs, dairy.
- Vitamin C:
- Function: Healing wounds, maintaining healthy skin, and immune function.
- Sources: Citrus fruits, tomatoes, strawberries.
- Vitamin D:
- Function: Absorption of calcium for healthy bones and teeth.
- Sources: Sunlight, fish, fortified milk.
- Vitamin A:
- Minerals:
- Calcium:
- Function: Builds strong bones and teeth, muscle function.
- Sources: Dairy products, leafy greens, fortified foods.
- Iron:
- Function: Essential for making hemoglobin in red blood cells.
- Sources: Red meat, beans, spinach.
- Calcium:
- Dietary Fibre (Roughage):
- Function: Aids digestion, prevents constipation.
- Sources: Whole grains, fruits, vegetables.
- Importance: Does not provide nutrients but helps in maintaining digestive health.
- Water:
- Function: Vital for all bodily functions, including digestion, waste removal, and temperature regulation.
- Sources: Drinking water, fruits, vegetables.
- Observation: Cutting fruits like tomatoes or lemons releases water.
3. Balanced Diet:
- Definition: A diet that includes all the necessary nutrients in the right proportions.
- Components: Carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, dietary fibres, and water.
- Benefits: Supports overall health, growth, and maintenance of body functions.
- Example Diet: Whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, fruits, vegetables, and plenty of water.
4. Deficiency Diseases:
- Definition: Diseases caused by the lack of essential nutrients over a long period.
- Examples:
- Vitamin A deficiency: Night blindness, poor vision.
- Vitamin B1 deficiency: Beri-beri (weak muscles, low energy).
- Vitamin C deficiency: Scurvy (bleeding gums, slow wound healing).
- Vitamin D deficiency: Rickets (soft bones, bent bones).
- Iron deficiency: Anemia (weakness, fatigue).
5. Healthy Eating Habits:
- Variety in Diet: Ensure a mix of different foods to get all nutrients.
- Portion Control: Avoid overeating and balance portion sizes.
- Reduce Junk Food: Limit foods high in fats, sugars, and salts.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Include Raw Foods: Eat raw fruits and vegetables to retain nutrients.
6. Cooking and Nutrient Loss:
- Nutrient Preservation: Some vitamins and minerals can be lost during cooking.
- Tips:
- Avoid overcooking vegetables.
- Wash fruits and vegetables before cutting.
- Use minimal water for cooking and do not discard cooking water.
- Include raw fruits and vegetables in the diet to retain Vitamin C.
7. Practical Activities:
- Food Diary: Track daily food intake to ensure a balanced diet.
- Nutrient Testing: Perform simple tests to identify the presence of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
- Diet Chart: Prepare a weekly balanced diet chart that includes a variety of foods.
Summary
- Nutrients: Carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, dietary fibres, and water are essential for our health.
- Balanced Diet: Important for maintaining good health and preventing deficiency diseases.
- Healthy Habits: Include a variety of foods, stay hydrated, and avoid nutrient loss during cooking.
By following these guidelines, students can ensure they receive a balanced intake of essential nutrients for their growth and overall health.
Here are 30 questions based on the provided text, including multiple-choice questions, fill-in-the-blanks, and short answer questions.
Multiple Choice Questions
- Which of the following is a major nutrient in our food?
- A. Water
- B. Carbohydrates
- C. Roughage
- D. All of the above
- Carbohydrates and fats are mainly known as:
- A. Body building foods
- B. Energy giving foods
- C. Protective foods
- D. Growth foods
- Which vitamin helps in maintaining good eyesight?
- A. Vitamin A
- B. Vitamin B
- C. Vitamin C
- D. Vitamin D
- Which nutrient is essential for the growth and repair of our body?
- A. Carbohydrates
- B. Proteins
- C. Fats
- D. Vitamins
- What is the test to identify starch in a food item?
- A. Iodine test
- B. Benedict’s test
- C. Biuret test
- D. Sudan III test
- An oily patch on paper indicates the presence of:
- A. Carbohydrates
- B. Proteins
- C. Fats
- D. Vitamins
- Which vitamin helps the body to use calcium for bones and teeth?
- A. Vitamin A
- B. Vitamin B
- C. Vitamin C
- D. Vitamin D
- What is the primary source of Vitamin D besides food?
- A. Sunlight
- B. Water
- C. Air
- D. Soil
- Which mineral is required for keeping our bones healthy?
- A. Iron
- B. Calcium
- C. Iodine
- D. Phosphorous
- What is the main function of roughage in our diet?
- A. Provide energy
- B. Aid digestion
- C. Build muscles
- D. Supply vitamins
Fill in the Blanks
- _____________ is caused by deficiency of Vitamin D.
Answer: Rickets - Deficiency of ______________ causes a disease known as beri-beri.
Answer: Vitamin B1 - Deficiency of Vitamin C causes a disease known as ______________.
Answer: Scurvy - Night blindness is caused due to deficiency of ____________ in our food.
Answer: Vitamin A - Proteins are also known as ____________ foods.
Answer: Body building - A balanced diet provides all the ____________ that our body needs.
Answer: Nutrients - Excess intake of ____________ can lead to obesity.
Answer: Fats - Dietary fibres are also known as ____________.
Answer: Roughage - Food items like rice and wheat are rich in ____________.
Answer: Carbohydrates - Lack of ____________ in diet can lead to anemia.
Answer: Iron
Name the Following
- Name two food items rich in fats.
Answer: Groundnuts, Butter - Name two food items rich in starch.
Answer: Potato, Rice - Name two food items rich in dietary fibre.
Answer: Whole grains, Vegetables - Name two food items rich in protein.
Answer: Eggs, Beans
Short Answer Questions
- What are the major nutrients in our food? Answer: Carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals.
- Why is a balanced diet important? Answer: A balanced diet provides all the nutrients that our body needs in the right quantities.
- What are deficiency diseases? Answer: Diseases that occur due to lack of nutrients over a long period.
- How can you test for proteins in a food item? Answer: By adding a few drops of copper sulphate and caustic soda to the food item and checking for a violet color.
- What is the role of water in our diet? Answer: Water helps absorb nutrients and remove waste from the body.
- What can happen if we wash vegetables after cutting them? Answer: It can result in the loss of vitamins and minerals.
Types of Nutrients in Food:
- This image illustrates the different types of nutrients found in food, including carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, dietary fibers, and water.

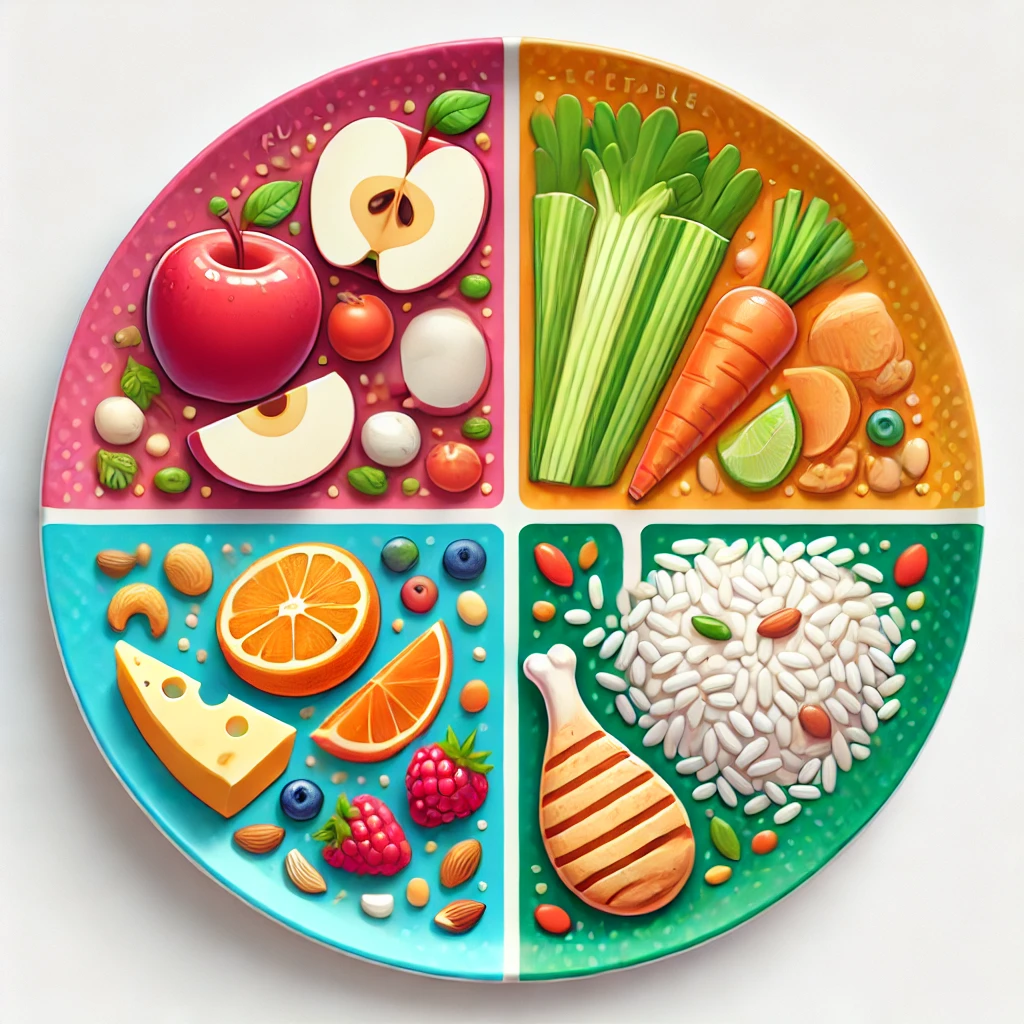
Here is the high-definition visual representation of a balanced diet plate designed for kids. The plate includes clearly defined sections for fruits, vegetables, grains, proteins, and a small section for fats, featuring colorful and engaging food items to appeal to children.

Here is the illustration depicting the process of testing for starch in food using iodine solution. The image shows a food sample with iodine solution being applied and turning blue-black, indicating the presence of starch. This clear and educational illustration is suitable for students learning about food components.
Here is the infographic highlighting deficiency diseases caused by the lack of vitamins and minerals. It depicts symptoms like night blindness, beri-beri, scurvy, and rickets alongside the respective deficient nutrients such as Vitamin A, Vitamin B1, Vitamin C, and Vitamin D. This clear and educational infographic is suitable for students, showing visual representations of both the diseases and the nutrient sources.

Here is the illustration showing different sources of dietary fiber, such as whole grains, fresh fruits, and vegetables. The image emphasizes their importance in a balanced diet with clear and colorful visuals of foods like oats, apples, carrots, and broccoli. This should help in understanding the key sources of dietary fiber and their role in nutrition.
